Charging an EV can be confusing for inexperienced EV drivers. There's a lot of technical jargon and confusing terminology that makes it hard to understand. We'll help you understand the differences between the types of chargers and ports.

What is an EV charger?
Technically, what most people call "EV chargers" are actually Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE). They basically convert the power to a format that the electric vehicle can accept; the charger itself is built into the car. That being said, the most popular term for these units that's seemed to stick is "EV chargers."
What types of EV chargers are there?
EV chargers fall into 3 basic categories; Level 1, Level 2 and Level 3.
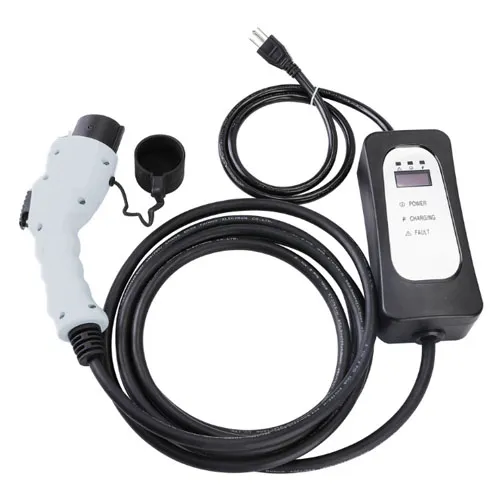

Level 1 Charger: 120-Volt
A Level 1 EV charger plugs into a standard outlet in your home to juice up your car. Usually, a level one charger can add 2 to 3 miles to your car for each hour they're used. Most electric vehicles in the US will come with a Level 1 charger.
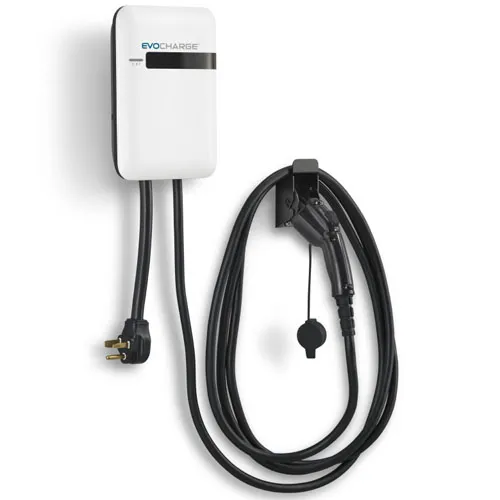


Level 2 Charger: 240-Volt
A Level 2 EV charger lets you charge up your electric vehicle around five times faster. These chargers use 240V or the type of outlet you see for an electric dryer or stovetop. They add between 12 and 60 miles to your battery each hour.
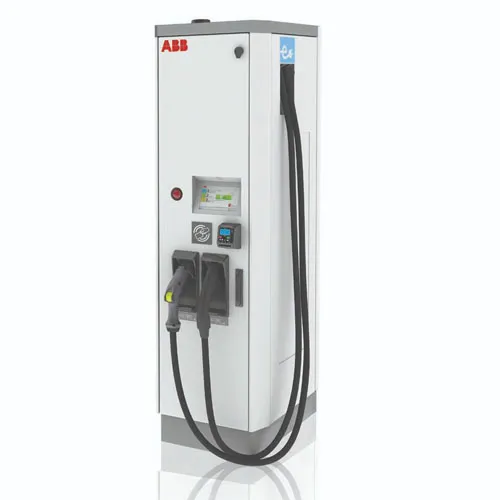


Level 3 Charger: 400-Volts or more
A Level 3 EV charger is the fastest type of EV charger. They're also called fast chargers, DCFC chargers or DC fast chargers. These units typically use 400V or more and add 150 miles to a battery in an hour. They're not very common in residential applications at this point.

Different EV charger connectors or plugs
An EV charger is connected to a vehicle by using a connector or plug. In the US, there are basically four main types:
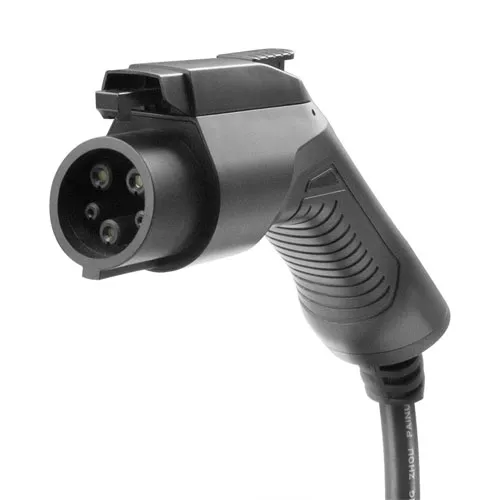

J1772 Plug
Level 1 and Level 2 Charging
The charging specification has been standardized across the US and Canada but has shifted recently. Up until 2024, almost every electric car uses a standardized plug called SAE J1772 for Level 1 and Level 2 charging. The only exception was Tesla that used a proprietary charging port.
In 2024, Tesla standardized their connector as the NACS connector and opened it up to automakers like Ford, Hyundai, and BMW. Starting with the 2025 model years, cars by many manufacturers will use the NACS connector. Adapters are available to convert between CCS and NACS for Level 2 charging.

J1772 Plug
Level 3 Charging
For Level 3, or fast charging, it gets a little more complicated. These types of chargers aren't typically found in home installations and are instead the fast chargers you'll see at offices, malls, shopping garages, etc. In North America, there are three types of connectors.
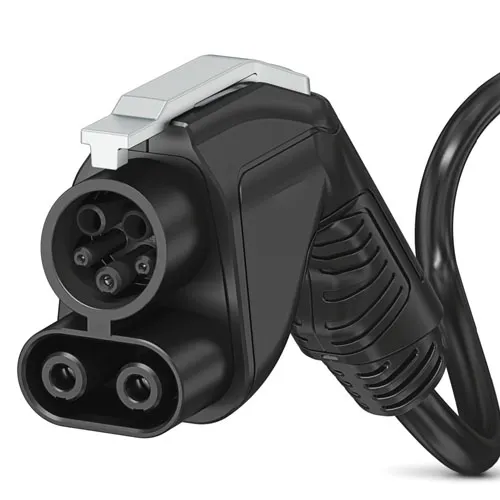

CCS (Combined Charging System)
Most EV cars sold in the US before 2025
This connector takes the standard J1772 plug and adds two more pins for high-speed charging. CCS is the most common connector in North America, and almost all North American automakers have agreed to use it.
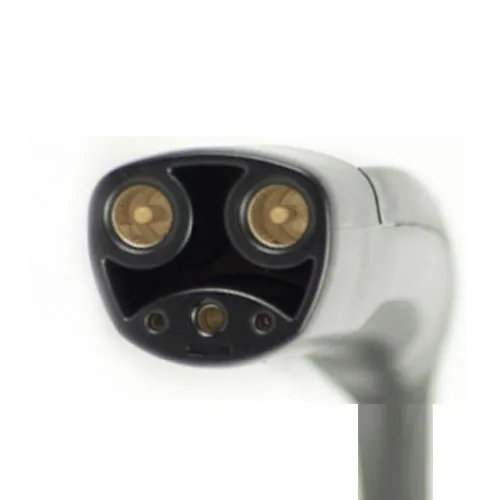

NACS
Teslas sold in the US and many 2025+ cars
Originally, this was called the Tesla connector but in 2024, it was standardized as the "NACS" connector and opened up to other automakers.
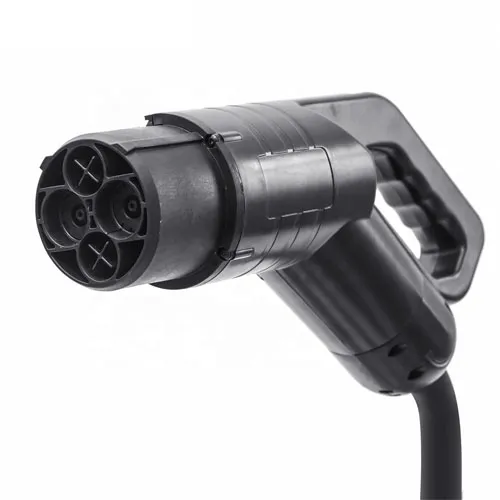

CHAdeMO
Nissan LEAF and Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV
This connector was developed in Japan and is popular there, but in the US, only the Nissan LEAF and Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV use the CHAdeMO connector.
Get rebates for installing an EV charger
To help offset the cost of installing an EV charger, a variety of rebates, incentives and grants are available across the US. Use the tool below to find out if you might qualify for any incentives for an EV Charger in your home.